Once in a while an insight will change the world. In this months Bank of England’s Quarterly Bulletin (2014 Q1), there is an article on money creation, and an primer on money. Actually these were pre-released on 12 March, and both are worth a read.
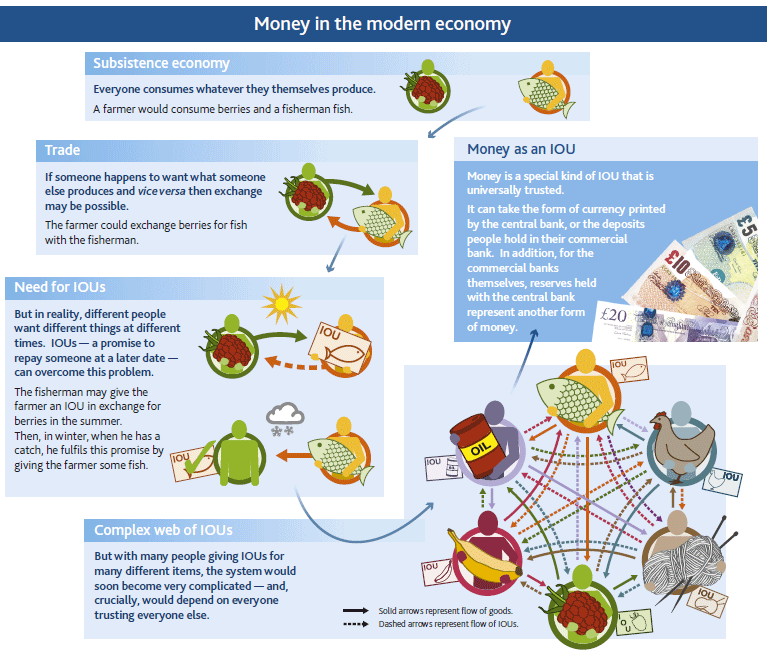
In the primer on money, we are reminded that it is essentially a trusted IOU and there are three main types, currency, bank deposits and central bank reserves. Each form is really an IOU between one sector of the economy and another. In the modern economy, most money is in the form of bank deposits, which are created by the commercial banks.
 You can see a video made by the bank here.
You can see a video made by the bank here.
The second article though is revolutionary, in that is has the potential to rewrite economics. “Money Creation in the Modern Economy” turns things on their head, because rather than the normal assumption that money starts with deposits to banks, who lend them on at a turn, they argue that money is created mainly by commercial banks making loans; the demand for deposits follows.
“In the modern economy, most money takes the form of bank deposits. But how those bank deposits are created is often misunderstood: the principal way is through commercial banks making loans. Whenever a bank makes a loan, it simultaneously creates a matching deposit in the borrower’s bank account, thereby creating new money. The reality of how money is created today differs from the description found in some economics textbooks:
• Rather than banks receiving deposits when households save and then lending them out, bank lending creates deposits.
• In normal times, the central bank does not fix the amount of money in circulation, nor is central bank money ‘multiplied up’ into more loans and deposits.
Although commercial banks create money through lending, they cannot do so freely without limit. Banks are limited in how much they can lend if they are to remain profitable in a competitive banking system. Prudential regulation also acts as a constraint on banks’ activities in order to maintain the resilience of the financial system. And the households and companies who receive the money created by new lending may take actions that affect the stock of money — they could quickly ‘destroy’ money by using it to repay their existing debt, for instance. Monetary policy acts as the ultimate limit on money creation. The Bank of England aims to make sure the amount of money creation in the economy is consistent with low and stable inflation. In normal times, the Bank of England implements monetary policy by setting the interest rate on central bank reserves. This then influences a range of interest rates in the economy, including those on bank loans. In exceptional circumstances, when interest rates are at their effective lower bound, money creation and spending in the economy may still be too low to be consistent with the central bank’s monetary policy objectives. One possible response is to undertake a series of asset purchases, or ‘quantitative easing’ (QE). QE is intended to boost the amount of money in the economy directly by purchasing assets, mainly from non-bank financial companies. QE initially increases the amount of bank deposits those companies hold (in place of the assets they sell). Those companies will then wish to rebalance their portfolios of assets by buying higher-yielding assets, raising the price of those assets and stimulating spending in the economy. As a by-product of QE, new central bank reserves are created. But these are not an important part of the transmission mechanism. This article explains how, just as in normal times, these reserves cannot be multiplied into more loans and deposits and how these reserves do not represent ‘free money’ for banks.”
They made a video which explains some of the key concepts.
This could be seen as a self-justification for the years of QE, and low interest rates in the UK, but I think it is really a radical insight. The world of money just changed!
